Mastitis in Cows and Buffaloes: How ABST-Guided Levofloxacin & Gentamicin Save More Animals Than Blind Costly Antibiotics
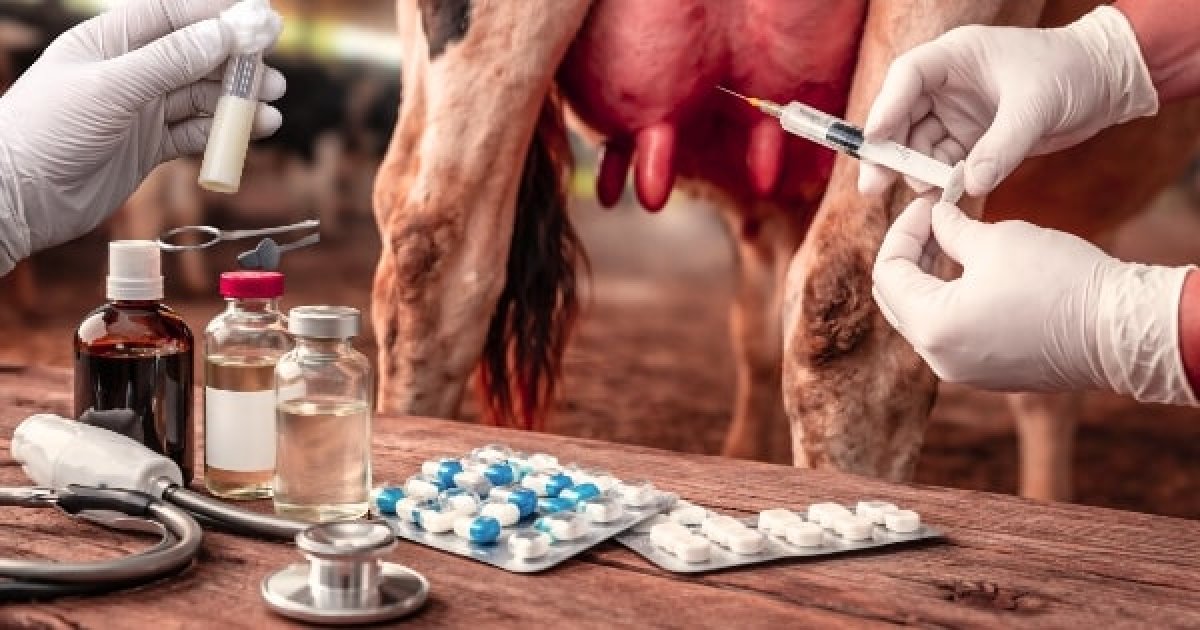
Why ABST is essential in mastitis treatment? Correct milk sampling, antibiotic resistance, and vet-guided Levofloxacin & Gentamicin explained.
Mastitis in Cows and Buffaloes: How ABST-Guided Levofloxacin & Gentamicin Save More Animals Than Blind Costly Antibiotics
Note: This article is written primarily for Registered Veterinarians, but in farmer-friendly language so that progressive dairy farmers can also understand the science behind correct treatment decisions.
1. Mastitis – Not Just “Udder Swelling” but a Systemic Disease
Mastitis is inflammation of the mammary gland, usually caused by bacterial infection. It is one of the most economically destructive diseases of dairy animals worldwide. Mastitis does not only reduce milk yield but also:
- Damages milk quality and shelf life
- Increases somatic cell count (SCC)
- Predisposes to repeat infections
- Causes infertility, weight loss, and sometimes death due to septicemia
In many herds today, mastitis has become difficult to treat because of increasing antibiotic resistance.
2. Major Causative Bacteria (Approximate Field Prevalence)
- Staphylococcus aureus – 35–45%
- Streptococcus spp. – 20–30%
- Coliforms (E. coli, etc.) – 15–20%
- Klebsiella, Pseudomonas – 5–10%
Each pathogen has a different antibiotic sensitivity pattern, therefore one single antibiotic can never be effective in all cases.
3. Why Do Expensive Antibiotics Fail?
- Blind routine use of Ceftriaxone, Cefoperazone, Amoxiclav etc.
- Incomplete treatment courses
- Ignoring intramammary therapy
- Lack of laboratory diagnosis
This has resulted in widespread resistance. Hence many farms report treatment failure even after using very costly antibiotics.
4. What is ABST?
ABST (Antibiotic Sensitivity Test) identifies the causative bacteria and shows which antibiotics can kill that organism and which cannot.
In simple words:
- Blind treatment = Guessing the key for a lock
- ABST-guided treatment = Using the correct key for that lock
5. Correct Milk Sampling for ABST (5 ml Syringe Method)
- Wash and dry the teat thoroughly
- Disinfect teat end with spirit/iodine
- Discard first 1–2 streams of milk
- Collect 5 ml milk directly in a sterile disposable syringe
- Cap the syringe, label with cow number, quarter, and date
- Send to lab within 6–12 hours (keep chilled)
Syringe collection gives minimum contamination and maximum accuracy.
6. Severity Classification (Field Practical)
- Mild: Milk flakes only
- Severe: Udder pain, fever 102–104°F
- Toxic: Depression, watery milk, dehydration, shock signs
7. Why Levofloxacin + Gentamicin Works in Many ABST-Positive Cases
Levofloxacin
- Excellent tissue penetration
- Controls systemic infection
- Once daily dosing
- Concentration-dependent bacterial killing
Gentamicin
- Rapid local bacterial killing
- Deep udder tissue penetration
- Often remains sensitive even when cephalosporins fail
- Cost-effective
Gentamicin must be used strictly under veterinary supervision due to renal toxicity risk and withdrawal period.
8. Supportive Management – Without This, Antibiotics Alone Fail
- Frequent stripping (4–6 times/day)
- Strict milking hygiene
- NSAIDs for pain and fever
- Fluids and calcium in severe cases
- Good nutrition and mineral supplementation
9. Message to Dairy Farmers
- Never self-medicate antibiotics
- Ask your veterinarian for ABST testing
- Discard milk during treatment
- Complete full course of therapy
- Improve milking hygiene to prevent recurrence
Conclusion
Modern mastitis treatment is not about using the strongest antibiotic, but about using the right antibiotic based on ABST. In many resistant mastitis cases, Levofloxacin and Gentamicin have proven to be faster, cheaper and more effective when selected scientifically.
Legal & Ethical Disclaimer
This article is intended only for Registered Veterinarians. Dairy farmers must not use antibiotics without veterinary supervision. Indiscriminate antibiotic use is dangerous, illegal, and promotes drug resistance.
